The most crucial thing is to balance it when we are talking about how to prepare a balance sheet. No, it’s not. There are some important points to follow to get accurate results. Here, you go. In this article, you will get clear insights on how to prepare it and easily balance it.
What Is Balance Sheet?
In This Article
ToggleBasically, Balance sheet balances an accounting equation. It tells us what we have in our hands or what we owes at the end of an accounting period. It is also known as Statement of financial position. It shows overall health of the business at a specific point. It can be prepared monthly, quarterly, and annually. More importantly, it is one of the critical financial statement including income statement and cash flow statement.
Simply put, balance sheet is a financial statement that depicts true financial position at a specific point in time.
Balance sheet comprises on an accounting equation:
Accounting equation:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
What We Have In Our Hands = What We Owes + Shareholder Equity
Not taking your too much time. Let’s strait jump toward our main topic: How to prepare a Balance sheet.
Balance Sheet Format
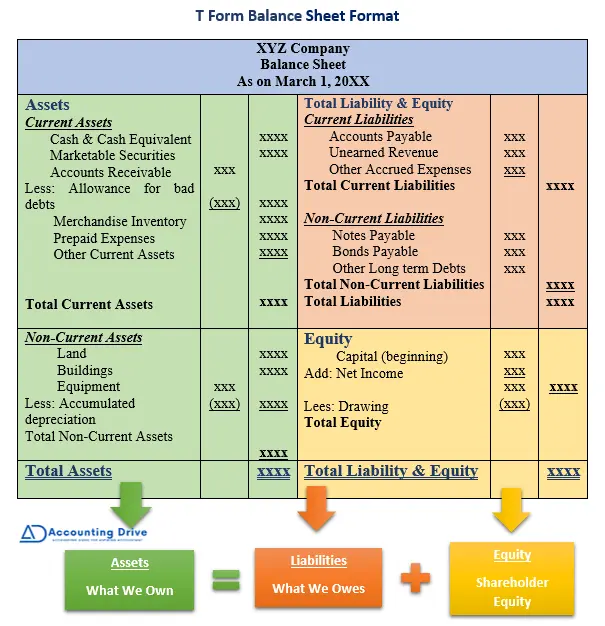
You can prepare balance sheet in two ways: the classified balance sheet or the T Form Balance sheet. Here, you can see both formats. There is no hard or fast rule, you can choose any format to prepare it. It’s up to you.
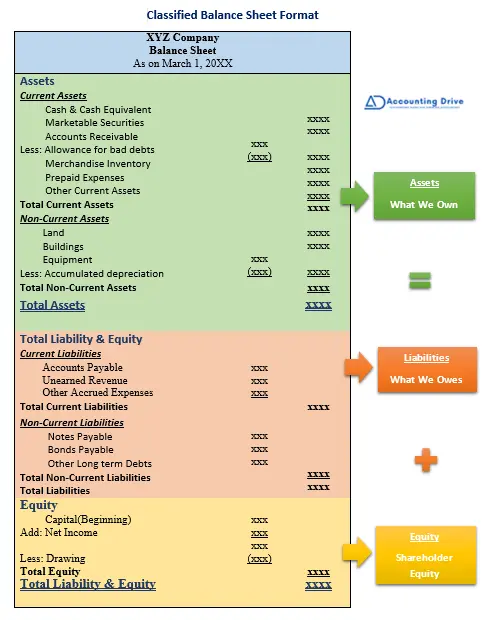
Classified Format
T Form Format
Steps to Prepare a Balance Sheet
It’s very easy to prepare a balance sheet because it requires only 8 steps to follow:
- 1st Step: Calculate Total Current Assets
- 2nd step: Calculate Total Non-current Assets
- 3rd Step: Calculate Total Assets
- 4th Step: Calculate Total Current Liabilities
- 5th Step: Calculate Total Non-Current Liabilities
- 6th Step: Calculate Total Liabilities
- 7th Step: Calculate Total Equity
- 8th Step: Calculate Total Liability & Equity
A Balance sheet can be divided into three main parts – Assets, Liabilities and equity: just as we have discuss earlier. First three steps will help us to get total assets, and other three steps will tell us how to calculate total liabilities and the last two steps will get us the final results. Now let’s start.
1st Step: Calculate Total Current Assets
The first step is to calculate total current assets. Current assets are those assets that are convertible to cash within a one year. It includes cash & cash equivalents, marketable securities, account receivable, prepaid expenses and more. You can calculate it by simply following these steps:
Current Assets
Cash & Cash Equivalent xxx
Marketable Securities xxx
Accounts Receivable xxx
Less: Allowance for bad debts (xxx) xxx
Merchandise Inventory xxx
Prepaid Expenses xxx
Other Current Assets xxx
Total Current Assets xxx
2nd step: Calculate Total Non-current Assets
The second step is the calculation of non-current assets. Non-current are also known as fixed assets, these takes two or more years to convert into cash. It includes Property, plant and equipment. You can calculate it as:
Non-Current Assets
Land xxx
Buildings xxx
Less: Accumulated Depreciation (xxx) xxx
Equipment xxx
Less: Accumulated depreciation (xxx) xxx
Total Non-Current Assets xxx
3rd Step: Calculate Total Assets
Now, what you have calculated earlier, add them both to get total assets.
Total Assets
Current Assets xxx
Add: Non-Current Assets xxx
Total Assets xxx
4th Step: Calculate Total Current Liabilities
Now, moving toward second main part: calculation of total liabilities. Here, Current liabilities are those liabilities that are payable within one year. It includes accounts payable, unearned revenue and all other accrued expenses.
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable xxx
Unearned Revenue xxx
Bank overdraft xxx
Other Accrued Expenses xxx
Total Current Liabilities xxx
5th Step: Calculate Total Non-Current Liabilities
The fifth step calls for the calculation of total non-current liabilities. Non-current liabilities are those liabilities that are due after one year. It includes debenture payable, and other long term liabilities.
Non-Current Liabilities
Notes Payable xxx
Bonds Payable xxx
Other Long term Debts xxx
Total Non-Current Liabilities xxx
6th Step: Calculate Total Liabilities
To calculate total liabilities, add current and non-current liabilities.
Total Liabilities
Current Liabilities xxx
Add: Non-Current Liabilities xxx
Total Liabilities xxx
7th Step: Calculate Total Equity
It’s our last main part, calculation for the total equity. Equity is left over amount reducing all liabilities. It shows the overall book value of a company. I is calculated as:
Equity
Capital (beginning) xxx
Add: Net Income xxx
xxx
Lees: Drawing (xxx)
Total Equity xxx
8th Step: Calculate Total Liability & Equity
The last steps requires to add total liability and equity. Pic data from the previous 6th and 7th step, add total liabilities and equity.
Total Liability & Equity
Total Liabilities xxx
Add: Total Equity xxx
Total Liability & Equity xxx
At last, you will get the equal balances on both sides.
Solved Example
Let’s take a simple example first.
Here is the selected data from the trail balance of Haram Enterprises as on December 31 XXXX:
- Cash $45,000
- Accounts payable 32,000
- Equipment 100,000
- Drawing 12,000
- Accumulated depreciation (equipment) 27,000
- Capital 450,000
- Merchandise inventory 27,000
- Bank overdraft 5,000
- Accounts receivable 30,000
- Land 300,000
With the help of this available data, you can easily prepare a balance sheet.
Haram Enterprises
Balance Sheet
As on December 31, XXXX
Assets |
| $ | Liabilities & Equity | $ |
Current Assets |
|
| Current Liabilities |
|
Cash |
| 45,000 | Accounts Payable | 32,000 |
Account Receivable |
| 30,000 | Bank Overdraft | 5,000 |
Merchandise Inventory |
| 27,000 |
|
|
Total Current |
| 102,000 | Total Liabilities | 37,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Non-Current Assets |
|
| Equity |
|
Land |
| 300,000 | Capital | 450,000 |
Equipment | 100,000 |
| Less: Drawing | (12,000) |
Less: Accumulated Depreciation | (27,000) | 73,000 |
|
|
Total Non-Current Assets |
| 373,000 | Total Equity | 438,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
Total Assets |
| $475,000 | Total Liability & Equity | $475,000 |
Key Points
- Balance sheet depicts the overall position of a company at a specific point in time.
- It tell us what we own and what we owes.
- It has three border categories: Assets, Liabilities and equity.
- It works on accounting equation.